Recent news has renewed interest in Haj Amin al-Husseini, the Mufti of Jerusalem and founder of Palestinian nationalism, and has also shined a spotlight on the ties between Palestinian nationalism and Nazism. Here is what you need to know:

- Husseini used the “Temple Mount Images” to convince the Arabs to massacre Jews in Hebron , in 1929.
The Atlantic’s reminded us last week, in an article of Jeffrey Goldberg; how Husseini’s incitement against Jews before the creation of the State of Israel served as a model for the current terror against Jews in Israel.
The spiritual leader of Palestine’s Muslims, the mufti of Jerusalem, Amin al-Husseini, incited Arabs in Palestine against their Jewish neighbors by arguing that Islam itself was under threat. (Husseini would later become one of Hitler’s most important Muslim allies.) Jews in British-occupied Palestine responded to Muslim invective by demanding more access to the Wall, sometimes holding demonstrations at the holy site. By the next year, violence directed against Jews by their neighbors had become more common: Arab rioters took the lives of 133 Jews that summer; British forces killed 116 Arabs in their attempt to subdue the riots. In Hebron, a devastating pogrom was launched against the city’s ancient Jewish community after Muslim officials distributed fabricated photographs of a damaged Dome of the Rock, and spread the rumor that Jews had attacked the shrine.
The current “stabbing Intifada” now taking place in Israel—a quasi-uprising in which young Palestinians have been trying, and occasionally succeeding, to kill Jews with knives—is prompted in good part by the same set of manipulated emotions that sparked the anti-Jewish riots of the 1920s: a deeply felt desire on the part of Palestinians to “protect” the Temple Mount from Jews.
2) Husseini had an intense working relations with Adolf Eichmann concerning the extermination of Jews in the Holocaust.
At the trial of Adolf Eichmann, one of the chief architects of the Holocaust, the testimony of convicted Nazi war criminal Dieter Wisliceny was used and clearly showed that Eichmann had close ties with Husseini:
Mr. Steiner [the prosecutor] first tells us that Wisliceny described his talks with Eichmann, why Palestine cannot be considered as the destination for emigration: “When I asked him why, he laughed and asked whether I had never heard of the Grand Mufti Husseini. He explained that the Mufti has very close contact and cooperation with Eichmann, and therefore Germany cannot agree to Palestine being the final destination, as this would be a blow to Germany’s prestige in the Mufti’s eyes.”
Then he goes on: “At this further conversation Wisliceny gave me more details about the cooperation between Eichmann and the Mufti. The Mufti is a sworn enemy of the Jews and has always fought for the idea of annihilating the Jews. He sticks to this idea always, also in his talks with Eichmann” – and here we have one of the points about which Wisliceny has reservations – “who, as you know, is a German who was born in Palestine. The Mufti is one of the originators of the systematic destruction of European Jewry by the Germans, and he has become a permanent colleague, partner and adviser to Eichmann and Himmler in the implementation of this programme.”
3) Husseini during World War II was an intense propagandist for the Third Reich , and a clear anti-Allies speaker.
As the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum remind us on their website :
In exile between 1937 and 1945, al-Husayni, claiming to speak for the Arab nation and the Muslim world, sought an alliance with the Axis powers (Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy) based on their publicly recognizing 1) the independence of the Arab states; 2) the right of those states to form a union reflecting a dominant Muslim and specifically Arab culture; 3) the right of those states to reverse steps taken towards the creation of a Jewish homeland in Palestine; and 4) al-Husayni himself as the spiritual and political representative of this pan-Arab, Muslim entity. In exchange, al-Husayni collaborated with the German and Italian governments by broadcasting pro-Axis, anti-British, and anti-Jewish propaganda via radio to the Arab world; inciting violence against Jews and the British authorities in the Middle East; and recruiting young men of Islamic faith for service in German military, Waffen-SS , and auxiliary units. In turn, the Germans and the Italians used al-Husayni as a tool to inspire support and collaboration among Muslim residents of regions under Axis control and to incite anti-Allied violence and rebellion among Muslims residing beyond the reach of German arms.
4) Nazi support of Husseini led to radicalizing the Muslim world.
Matthias Küntzel, associate researcher of the Vidal Sassoon International Center for the Study of Anti-Semitism at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, showed that the Nazi support of Husseini and the Muslim Brotherhood played an important role in radicalizing the Muslim world.
In Zeesen, a town with some four thousand inhabitants to the south of Berlin, once stood one of the world’s most powerful shortwave transmitters. From 1939 onward, it broadcast its daily Arabic-language program. Of all the foreign-language services, the Oriental Service had “absolute priority. It reached out to Arabs, Turks, Persians, and Indians and had an eighty-strong staff, including freelance announcers and translators.”4 Between 1939 and 1945, at a time when, in the Arab world, listening to the radio took place primarily in public squares or bazaars and coffee houses, no other station was more popular than the Zeesen service, which skillfully mingled anti-Semitic propaganda with quotations from the Koran and Arabic music. The Allies in the Second World War were presented as lackeys of the Jews and the notion of the “United Jewish Nations” drummed into the audience. At the same time, the Jews were attacked as the worst enemies of Islam. “The Jew since the time of Mohammed has never been a friend of the Muslim, the Jew is the enemy and it pleases Allah to kill him.”5 Today, this same message is being put out on satellite by Hizbollah’s Al- Manar TV channel. So what are the historical connections between the shortwave transmitter in Zeesen and the Beirut satellite channel?
A highlight of Radio Zeesen’s output was the demand for jihad by the most popular figure in the Arab-Islamic world of the time, the Mufti of Jerusalem, Haj Amin el-Husseini (1895-1974). From 1941 onward he lived in Berlin, supervising Arabic radio broadcasting out of Zeesen, Athens, and Rome.6 Nobody promoted hatred of Jews among Muslims more effectively than the Mufti. The European responsibility for this is clear: el-Husseini had after all been appointed to and promoted in office by European powers. It was the British who, having first sentenced him to ten years in jail for anti-Jewish incitement in 1920, then amnestied him in 1921 and made him Mufti against the will of the majority of Palestinians. It was the Germans who paid him for his services between 1937 and 1945. And it was the French who in 1946, when the Mufti was being pursued internationally as a war criminal, helped him escape to Egypt and continue his activities.
5) Palestinian Nationalism and Modern Islamism were both influenced by Husseini’s radical and violent anti-Semitism ,that will later became a founding feature of these movements.
Küntzel continues:
Nobody had a greater influence on the early history of the Middle East conflict than the Mufti, who as president of the Supreme Muslim Council was not only the supreme religious authority but also the central figure in Palestinian nationalism. In the 1930s, there were countless Arab nationalists who viewed Germany as an ally against the British without concerning themselves with the nature of the Hitler regime. Things were different where the Mufti was concerned: he knew what the regime was about and was attracted to it for that very reason. …
Thus did the years 1936-1939 shape Islamism as a new and independent, anti-Semitic and antimodern mass movement. Until 1936 the moderate Arab forces, which welcomed or at least tolerated Zionism, had in no way been marginalized. This changed after the National Socialists threw their weight behind the Islamists. They successfully spurred on the unrest in Palestine and so contributed to spreading the idea that the Jews were the enemy to Egypt. The Islamist mass mobilization was financially and ideologically supported by Radio Zeesen and other means of propaganda. This was one of the reasons that it was the Islamism and anti-Semitism of Hassan al-Banna rather than the enlightened modernism of Kemal Atatürk that gained general acceptance in the Arab part of the Islamic world.35
The Zeesen shortwave transmitter appears in retrospect to have been the interface that transferred the anti-Semitic ideology to the Arab world and linked early Arab Islamism with late National Socialismzism. Although Radio Zeesen ceased operation in April 1945, it was only after that date that its frequencies of hate really began to reverberate in the Arab world.
6) Husseini’s “fusion” of European anti-Semitism with Islamic views of Jewish evil has been adopted by Islamists around the world.
In a 2009 article in The Wall Street Journal citing Küntzel’s work, Daniel Schwammenthal wrote that the mufti’s “fusion of European anti-Semtism—particularly the genocidal variety—with Koranic views of Jewish wickedness has become the hallmark of Islamists world-wide, from al Qaeda to Hamas and Hezbollah.”
During his time in Berlin, the mufti ran the Nazis’ Arab-language propaganda radio program, which incited Muslims in the Mideast to “kill the Jews wherever you find them. This pleases God, history and religion.” Among the many listeners was also the man later known as Ayatollah Khomeini, who used to tune in to Radio Berlin every evening, according to Amir Taheri’s biography of the Iranian leader. Khomeini’s disciple Mahmoud Ahmadinejad still spews the same venom pioneered by the mufti as do Islamic hate preachers around the world.
Muslim Judeophobia is not—as is commonly claimed—a reaction to the Mideast conflict but one of its main “root causes.” It has been fueling Arab rejection of a Jewish state long before Israel’s creation.
7) Husseini recruited thousands of Muslim soldiers for Hitler.
As the Holocaust Museum also noted, Husseini helped create a Bosnian-Muslim division of the Waffen-SS:
When the SS decided in February 1943 to recruit among Bosnian Muslims for a new division of the Waffen-SS, SS Main Office Chief Berger enlisted al-Husayni in a recruiting drive in Bosnia from March 30 and April 11. On April 29, Berger reported that 24,000–27,000 recruits had signed up and noted that the “visit of the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem had had an extraordinarily successful impact.” Both al-Husayni and the SS repeatedly referred to the success of the 13th Waffen-SS Mountain Division (also known as “Handschar”). Al-Husayni spoke to the military Imams of the division, stressing the importance of maintaining the principles of Islam and of “strengthening cooperation between the Muslims and their ally, Germany,” and identifying common enemies faced by Muslims and the Germans: World Jewry, England and its allies, and Bolshevism.
8) Husseini was designated by the UN as a war criminal.
The Jewish Telegraphic Agency reported on his placement on a UN war criminals register in July 1945:
Hadj Amin el-Husseini, former Grand Mufti of Jerusalem, has been officially placed on the war criminals list of the United Nations, the Hebrew Committee for National Liberation reported today. …
In reply to its original request to the War Crimes Commission that it place the Mufti on its list of criminals, the commission stated that before doing so one of its member governments would have to present evidence constituting a prima facie case.
Upon receipt of this cable, a committee representative discussed the matter with Ivan Subasic, Yugoslav Minister of Foreign Affairs, while he was at San Francisco, pointing out that the Mufti had organized the German S.S. Moslem Division in Bosnia and been responsible for the massacre of Yugoslav Moslems who refused to collaborate with the Germans.
9) After World War II, Husseini continued spreading anti-Semitic propaganda as a central tenet of Palestinian nationalism
Husseini escaped arrest and spent the last twenty-eight years of his life spreading anti-Semitic and anti-Israel propaganda. The Holocaust Museum recounts:
As the Nazi regime collapsed in 1945, French authorities took al-Husayni into custody. He escaped to Egypt in 1946. Al-Husayni devoted the remainder of his life to supporting Palestinian nationalism and to agitating against the State of Israel. He continued to produce and disseminate anti-Zionist, anti-Jewish, and anti-Israel propaganda. He died in Beirut, Lebanon, on July 4, 1974.
10) Husseini remains a hero to Palestinians.
In a January 2013 ceremony, Palestinian Authority President Mahmoud Abbas praised Husseini as a hero of the Palestinian cause :
On the anniversary of the [Fatah] Launch, we renew the promise to our blessed Martyrs, that we will follow the path of the Martyr Brother Yasser Arafat and his comrades among the leaders of all the fighting forces, all the Martyrs. … Now let us recall the pioneers: The Grand Mufti of Palestine, Haj Muhammad Amin Al-Husseini.











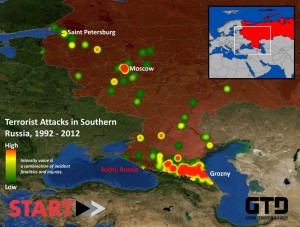 the effectiveness of the Islamic insurgency in the North Caucasus – a region that’s often referred to as “Russia’s soft belly.”
the effectiveness of the Islamic insurgency in the North Caucasus – a region that’s often referred to as “Russia’s soft belly.”









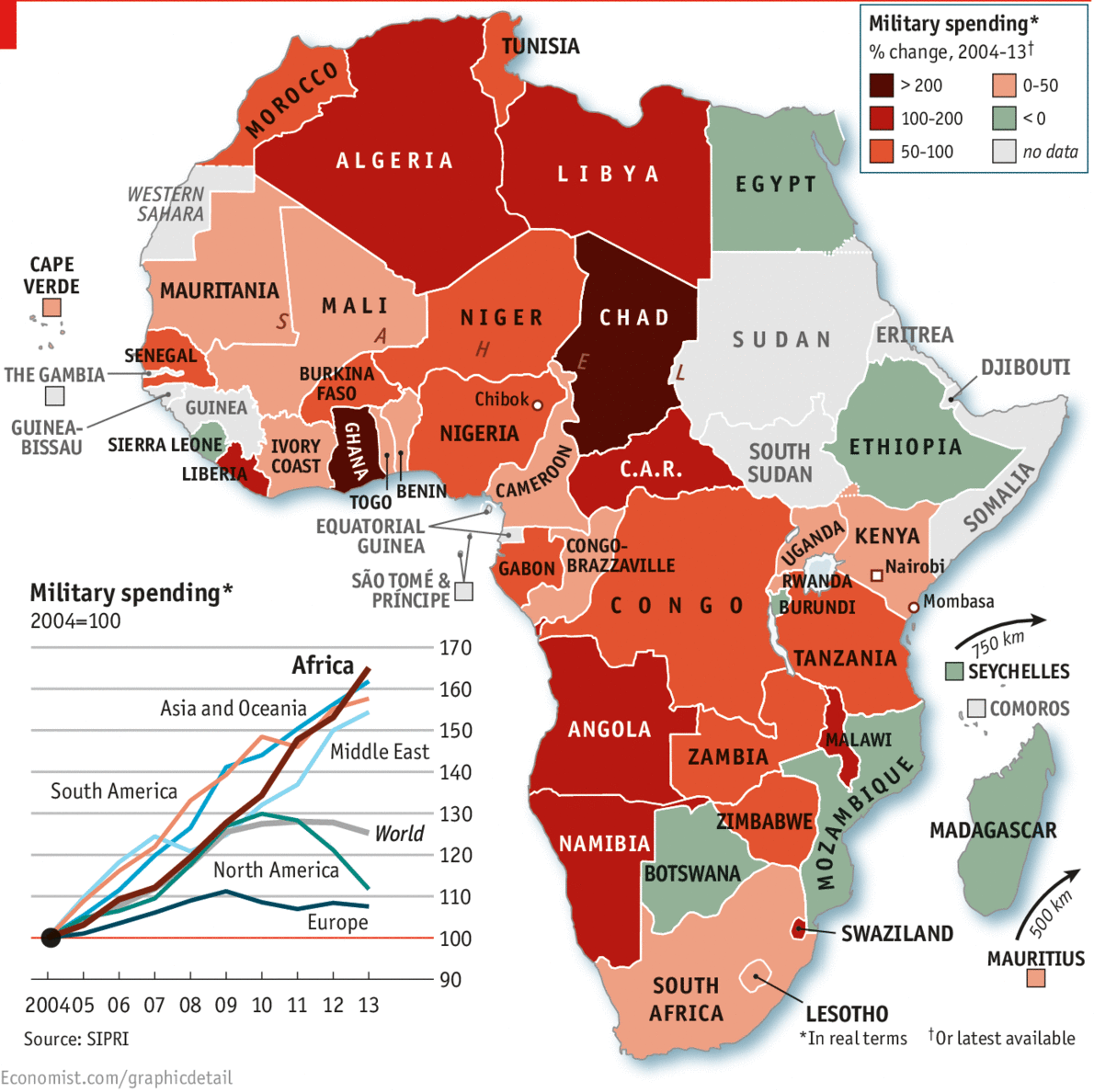
 ology industry in Angola remains limited but there is increasing awareness hence the country is getting on the right track when it comes to information and technology development . There may not have been a lot of ground breaking and jaw chattering inventions coming from the Angola but it is expected that with sustained growth and development , the counry would come up to be a tech giant in Africa.
ology industry in Angola remains limited but there is increasing awareness hence the country is getting on the right track when it comes to information and technology development . There may not have been a lot of ground breaking and jaw chattering inventions coming from the Angola but it is expected that with sustained growth and development , the counry would come up to be a tech giant in Africa.











 ool of former Lega Nord (see below), extreme-right and extreme-left wing voters at the sound of an anti-euro and anti-system ideology.
ool of former Lega Nord (see below), extreme-right and extreme-left wing voters at the sound of an anti-euro and anti-system ideology.
