Introduction
Russia’s military power potential, nuclear weapons and natural economic resources have allowed Russia to remain a great power. Alongside this, its recent influence in Syria and also Afghan Peace Process has made it evident to the world that Russia is not far behind to play its role in the changing world order.
Having influence in world power politics and world order policies, what are the power political strategies adopted by Russia – to play its role in the world order as a great power? This article addresses this question.
Power Political Strategies of Russia
- Economic Strategies
Even though, it’s part of BRICS but according to the World Bank statistics, the economic growth perspectives of Russia are negative. Economically it is dependent on the exports of oil and gas and due to low prices of oil and gas after the end of their boom in 2013 (BBC News, 2015), ongoing international sanctions and geopolitical tensions; Russia is in the recession situation (World Bank, 2015). Its GDP growth rate is also in decline as it has declined from 4.3% in 2011 to 0.6% in 2014 (World Bank Data, 2015). Sharma (2012) in this regard argues that among emerging economies (BRICS) Russia is the weakest. Furthermore, he argues about Russia’s being part of BRICS that despite the fact it is out of balance yet it is part of BRICS because the
term with an ‘R’ sounds better.
But according to the Centre for Strategic and International Strategies (CSIS), Russia’s economic situation has unexpectedly and rapidly changed contemporarily. When Putin became Russian President, it was effectively bankrupt. But its economy started improving after 2010.
However, according to Reuters Report (2019), Russia’s economic growth climbed to a six-year high in 2018. Moreover, according to World Bank’s Russia Economic Report (2018), there are modest growth prospects for Russia for 2018-2020. The growth forecast is at 1.5 – 1.8 per cent which can favorably be affected with higher than expected oil prices. Even under such modest growth scenario, Russia can achieve its goal of halving its poverty to 6.6 per cent by 2024.
An entitled, “Russia’s Great Power Strategy under Putin and Medvedev” report was published by Swedish Institute of International Affairs in 2010. While discussing the economy of Russia, it highlighted that the primary security aim for Russia is to be among top 5 leading countries in terms of GDP. In order to attain this by its own efforts, Russia is promoting its productivity, improving its innovation system and developing and modernizing its resources. Furthermore, the report discussed that the Russia’s economic strategy is to give state the regulating role, provide support to the companies which are abroad and counteract the prejudice against them and in order to invest in its advanced sectors, Russia aims to invite the foreign investors. This can be considered Russia’s geoeconomic strategy.
- Military Strategies
BBC News (2015) reports that in order to openly promote its apparent interests in the former states of Soviet Union, Russia adopted an insistent foreign policy stance in 2000s. This became apparent when Russia started military conflict with Georgia in August, 2008. In 2010, a new nuclear arms treaty resulted in a reset of Russia-US ties which replaced the expired Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (START). The February 2014 Ukrainian revolution which overthrew Ukrainian President and brought a Western inclined leader into power, gave rise to a more intense crisis between East and West, particularly after the Russian annexation of Crimea. Due
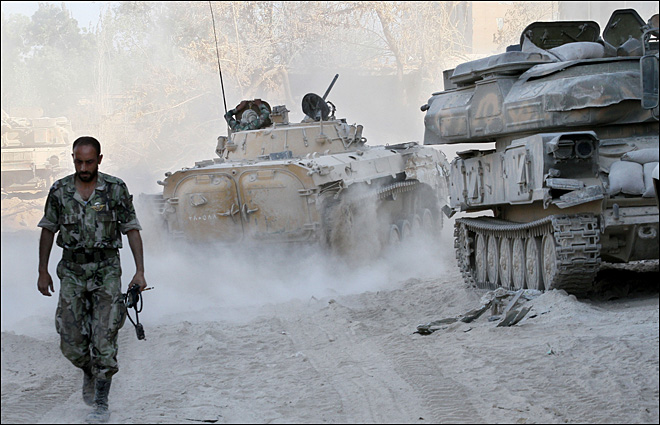
to this, Russia was accused by the US, EU and other Western States for supporting the Pro-Russian rebellious support in the east of Ukraine which resulted in imposed sanctions against individuals and businesses especially those close to Russian President Putin. In addition to this, due to Russia’s military support for Assad regime in Syria, some fear a new cold war (BBC News, 2015).
Even with no end in sight for the civil war in Syria, Assad Regime is in a good position because of the support from Russia as well as from Iran. Russia has built naval and air bases in Syria. Russia is said to have decided to turn one of the bases in Syria-Khmeimim base as its permanent military contingent stationed in Syria. Such ambitions show that Russia is no more
limited to its borders worrying about NATO forces in its backyard.
- Political Strategies
According to “Intelligence Risk Assessment 2015” published by “Danish Defense Intelligence Service”, in order to restore its role as a great power, Russia is ambitious to show its influence in the decisions of major global issues. In this regard, Russia is trying to recreate its influence on the non-NATO member countries and to achieve its intentional goals; it has showed its willingness and capability by the use of military power. Not only this, though predominantly for the disposition in local conflicts or wars in its borders, it has continuously been developing its armed forces. The report furthermore analysis that in order to deter the military presence of alliance of NATO in the Baltic countries, Russia attempts to influence the strategic balance in the Baltic Sea region. During the events of crisis in Baltic Countries, the report predicts the capability improvements of Russia to threaten the reinforcement of NATO.
The report, however, says that it is improbable that Russia is going to have a military confrontation with the NATO alliances. Despite its non-political intentions, the report in the coming years considers Russia as a substantial security challenge to the West and the NATO alliance.
Moreover, in Afghan Peace Process, Russia is also playing an increasing role as a mediator. Russia hosted Intra-Afghan meetings to play its role. In last six months, Russia hosted two meetings, first in February and the second on May. The meetings hosted by Russia brought together Afghan opposition politicians and Taliban leaders. However, the Afghan government representatives were not part of either of the meetings (Arab News, 2019). Is Russia planning to have long-term relations with Afghanistan by keeping the current government out of the talks? Probably, yes but the future political scenario of Afghanistan will divulge that. With its economic, political and military strategies, Russia’s emergence in the changing world
order is imminent. With other players like China, not an explicit seeker of hegemony, US, hegemon, and European Union, with its efforts to sustain globalisation effectively, a new cold war might take place. Russia can no longer be kept at bay when it comes to international politics.